What are the global settings?
The global settings available in ArcGIS GeoEvent Server allow you to configure GeoEvent Server to properly align with different deployments. For example, you may want to configure proxy settings for internet access, set the frequency of automated backups, or increase the maximum supported message sizes.
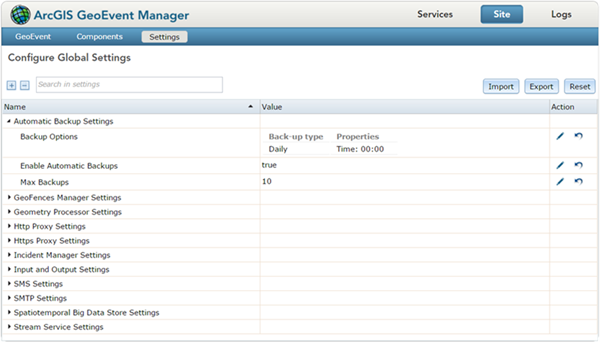
Overview of the global settings
Below you will find an overview of the global settings available in GeoEvent Server. Some settings may require additional information from your IT department or third party vendors to properly configure. Settings that have been incorrectly set may result in reduced functionality and/or data loss.
Automatic Backup Settings
The Automatic Backup Settings allow you to enable or disable scheduled backups of the entire GeoEvent Server configuration. Automatic backups are enabled by default, a backup will occur daily at 12AM with up to 10 days of configurations stored. Configure the Automatic Backups folder under Site > GeoEvent > Data Stores. A backup can be scheduled to run daily, weekly, or monthly. The Max Backup setting allows for storing an N-Number of configurations. Once the maximum number of configurations exist, GeoEvent Server will automatically start deleting the oldest file.

Geofence Manager Settings
The Geofence Manager Settings allow you to configure options for the spatial operators, geometric precision, and data storage considerations for geofences.
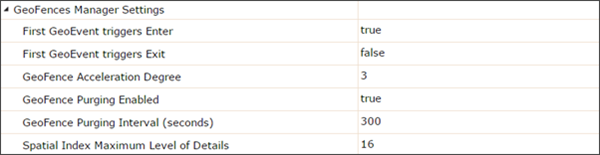
- First GeoEvent triggers Enter - Used in conjunction with the spatial filtering processors (e.g. filter, GeoTagger, Incident Detector, and more) to determine if the first GeoEvent of a defined track appears inside a geofence and whether an enter Enter condition should be triggered. The default is true.
- First GeoEvent triggers Exit - Used in conjunction with the spatial filtering processors (Filter, GeoTagger, Incident Detector, etc.) to determine if the first GeoEvent of a defined track appears outside a geofence and whether an Exit condition should be triggered. The default is false.
- Geofence Acceleration Degree - The resource priority given to spatial evaluations. The value is a non-negative whole number between 0 and 3. Higher values represent increased usage speed at the cost of longer initial loading time and higher memory consumption. The default is 3.
- 0 - No acceleration
- 1 - Mild acceleration (consumes the least amount of memory)
- 2 - Medium acceleration (consumes more memory and takes more time to accelerate when adding a geofence, but may work faster)
- 3 - High acceleration (consumes the most memory and takes the longest time to accelerate when adding a geofence, but may work faster than the others)
- Geofence Purging Enabled - Determines if an expired geofence (based on the END_TIME tagged field) is automatically removed. The default is false.
- Geofence Purging Interval (seconds) - Used in conjunction with the Geofence Purging Enabled setting to define an interval to check for expired geofences. The default is 300 seconds.
- Spatial Index Maximum Level of Detail - The level of precision of stored geofence geometries. A higher value results in an index that is more effective for smaller geographic areas (smaller geofences), however, the higher the value, the more memory that will be consumed. The value should be between 4 and 32, the default value is 16.
Geometry Processor Settings
The Geometry Processor Settings allow administrators the ability to enable or disable selectable linear units for use in the processors available in GeoEvent Server.

HTTP Proxy Settings
The HTTP Proxy Settings allow administrators to configure GeoEvent Server to access online resources through an HTTP Proxy. This is typically an internal site users must first authenticate against before connecting to the Internet.
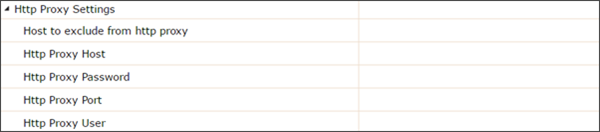
- Host to exclude from HTTP proxy - The hosts that should be accessed without going through the HTTP proxy. Typically, this defines internal hosts. The value of this property is a list of hosts, separated by the ''|'' character. In addition, the wildcard character ''*'' can be used for pattern matching. For example, http.nonProxyHosts="*.foo.com|localhost" will indicate that every host in the foo.com domain and the localhost should be accessed directly even if a proxy server is specified.
- HTTP Proxy Host - The hostname, or address, of the HTTP proxy server.
- HTTP Proxy Password - The password to present to the server if the proxy requires authentication.
- HTTP Proxy Port - The port number of the HTTP proxy server.
- HTTP Proxy User - The user to pass to the server if the HTTP proxy requires authentication.
HTTPS Proxy Settings
The HTTP Proxy Settings allow administrators to configure GeoEvent Server to access online resources through an HTTPS proxy. This is typically an internal site that users must first authenticate against before connecting to the internet. These settings are functionally the same as the HTTP Proxy Settings but are secured using SSL communication.
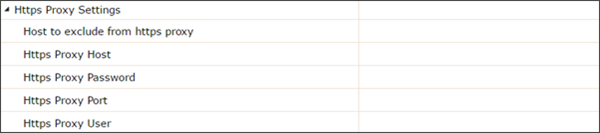
- Host to exclude from HTTPS proxy - The hosts that should be accessed without going through the HTTPS proxy. Typically, this defines internal hosts. The value of this property is a list of hosts, separated by the ''|'' character. In addition, the wildcard character ''*'' can be used for pattern matching. For example https.nonProxyHosts="*.foo.com|localhost" will indicate that every hosts in the foo.com domain and the localhost should be accessed directly even if a proxy server is specified.
- HTTPS Proxy Host - The hostname, or address, of the HTTPS proxy server.
- HTTPS Proxy Password - The password to present to the server if the proxy requires authentication.
- HTTPS Proxy Port - The port number of the HTTPS proxy server.
- HTTPS Proxy User - The user to pass to the server if the HTTPS proxy requires authentication.
Incident Manager Settings
The Incident Manager Settings define the maximum number of closed and open incidents for use within the Incident Detector Processor. By default, the Incident Detector Processor can retain the current state of 1000 open and 1000 closed incidents. Increasing the values allows you to monitor additional TRACK_ID tagged events, however, it will result in additional memory usage.

Input and Output Settings
The Input and Output Settings allow you to configure the Input Buffer Capacity (MB). This value determines the maximum message size (in MB) that can be maintained in memory for an input. Large batches of events or those with highly complex geometries can sometimes exceed the default setting of 20. The value should be set between 1 and 2047. Any changes to this setting will not be reflected in existing inputs and a restart of the ArcGIS GeoEvent Server service is recommended.

SMS Settings
The SMS Settings provide the Short Message Service (SMS) endpoints for most cellular carriers. When sending a text message, the output is automatically populated using these settings to include [email protected], (for example, for Verizon it would be [email protected]). The endpoints can be updated and new carriers added.

SMTP Settings
The SMTP Settings allow administrators to configure the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) connection details specific to an organization. This is used in conjunction with the Send an Email Output Connector and should be configured per an organization's system administrator or IT department.
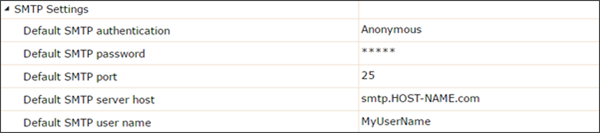
- Default SMTP authentication - The authentication method used to connect to the SMTP server (Anonymous, SSL, or TLS).
- Default SMTP password - The password to present to the server if the authentication method requires credentials.
- Default SMTP port - The port number of the SMTP server.
- Default SMTP server host - The hostname, or address, of the SMTP server.
- Default SMTP user name - The user name to present to the server if the authentication method requires credentials.
Spatiotemporal Big Data Store Settings
The Spatiotemporal Big Data Store Settings define the default settings when creating new spatiotemporal big data store data sources. The values can be changed in the publishing dialog in GeoEvent Manager.

- Default Number of Shards - The default number of shards a spatiotemporal big data store's data will be divided into. It is recommended the value be set to the number of nodes in a spatiotemporal big data store cluster, however it should never exceed the number of nodes. Acceptable values are 1 to N, with a default value of 3.
- Default Replication Factor - The default replication factor used when publishing to the spatiotemporal big data store. Acceptable values are 0 to N, where N is the maximum number of spatiotemporal big data store machines.
Stream Service Settings
The Stream Service Settings allow you to adjust multiple aspects of the stream services connection details and message sizes.
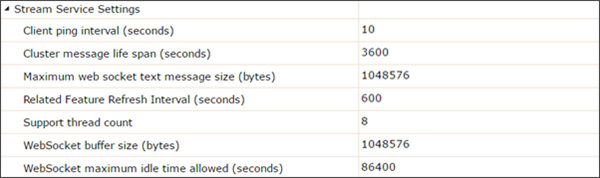
- Client ping interval (seconds) - Defines how often (in seconds) the server will ping all clients to make sure they are awake and will let them know the server is awake (even if there is no data flowing). Clients should respond with a ping to stay connected (most browsers handle this automatically). Clients should not set their timeout period shorter than this value or they might disconnect themselves. Value must be between 1 and 2,073,600 (24 days).
- Cluster message life span (seconds) - Defines how long (in seconds) a message can be held by an ArcGIS cluster waiting for clients to consume it. Messages in the cluster that have not been processed in this amount of time will be purged. Value must be between 0 and 2,073,600 (24 days).
- Maximum web socket text message size (bytes)- Defines the maximum size (in bytes) that a text message can be when sent through a WebSocket. Text messages larger that this cannot be delivered. Value must be between 1 and 2,147,483,647 (2GB).
- Related Feature Refresh Interval (seconds) - Defines how often (in seconds) the server should periodically query the feature service to see what features are in the spatial filter. Applicable when a related feature service is selected when publishing a stream service and a spatial filter is added from the client side.
- Support thread count - The number of threads used to manage all client connections. This provides better isolation so that slow clients do not affect other clients. The more threads used, the more server resources will typically be consumed. Value must be between 1 and 100.
- WebSocket buffer size (bytes) - The size (in bytes) a WebSocket allocates to hold data in transit (data that has been sent, but not read by the receiver). Value must be between 1 and 2,147,483,647 (2GB).
- WebSocket maximum idle time allowed (seconds)- The maximum amount of time (in seconds) the server will keep idle client connections before disconnecting them. Value must be between 1 and 2,073,600 (24 days).